What is Lidar?
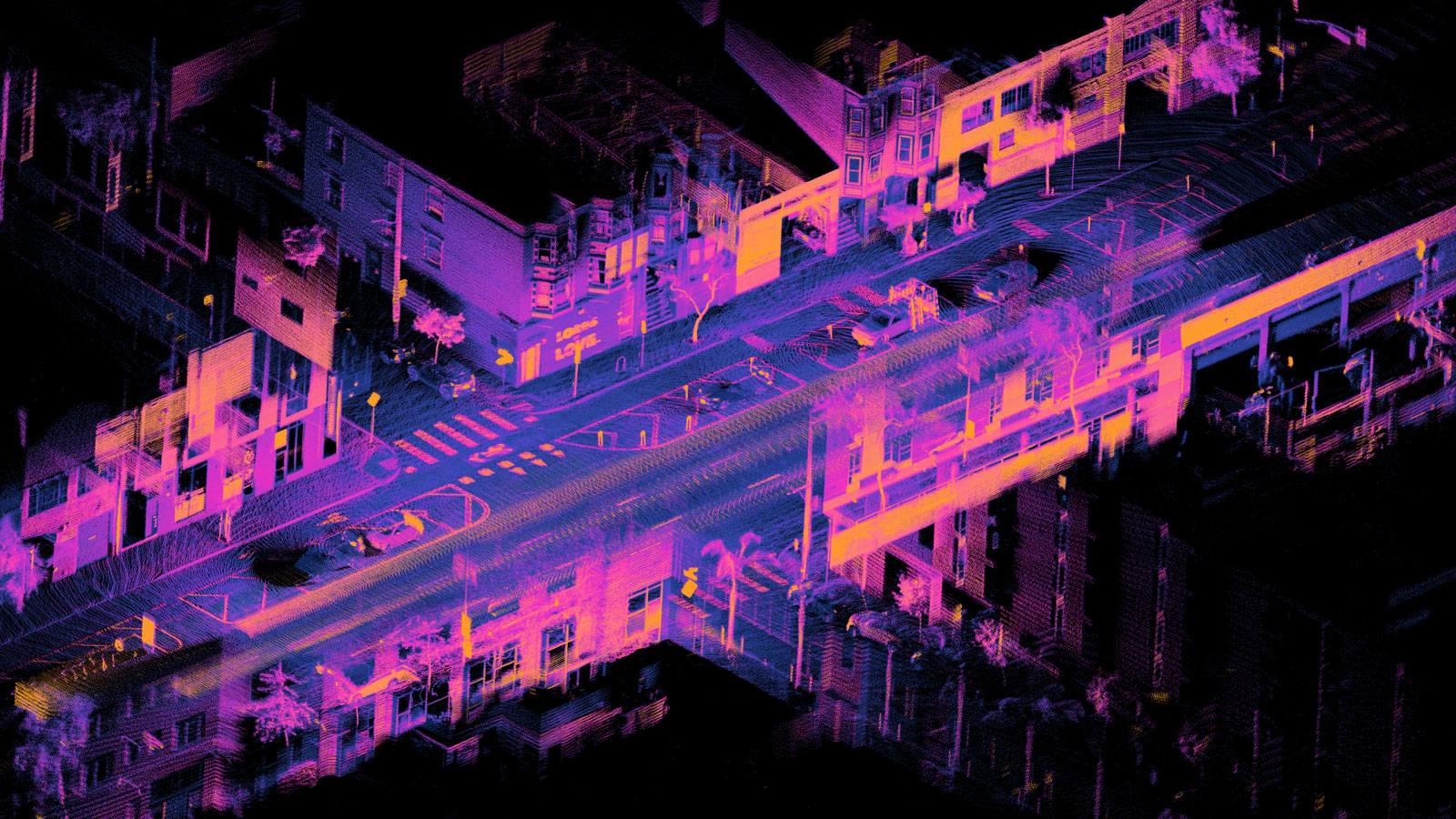
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) is a remote sensing technology that uses light, typically pulsed laser light, to measure distances to objects. This technology is used to create highly accurate 3D maps of the Earth’s surface, including vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
How Does Lidar Work?
A LiDAR system emits laser pulses and measures the time it takes for the pulses to return after reflecting off objects. By knowing the speed of light, the system can calculate the distance to the object. This process is repeated millions of times per second, creating a dense point cloud of 3D data.
Applications of Lidar
Lidar has a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
- Mapping and Surveying: Lidar is used to create detailed topographic maps, digital terrain models, and city models.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Lidar sensors provide real-time information about the environment, enabling self-driving cars to navigate safely.
- Forestry and Agriculture: Lidar helps measure tree height, biomass, and forest health.
- Archaeology and Heritage Preservation: Lidar can reveal hidden archaeological sites and monitor the condition of historical structures.
- Urban Planning: Lidar data is used for urban planning, infrastructure development, and disaster management.
- Environmental Monitoring: Lidar is used to study glaciers, coastal erosion, and climate change.
Types of Lidar
There are two main types of LiDAR:
- Ground-Based LiDAR: This type of LiDAR is mounted on a tripod or vehicle and is used to scan specific areas.
- Airborne LiDAR: Airborne LiDAR is mounted on aircraft or drones and can cover large areas quickly.
Advantages of Lidar
- High Accuracy: Lidar provides highly accurate measurements, even in challenging environments.
- Versatility: Lidar can be used in a wide range of applications.
- Speed: Lidar can collect data quickly, making it suitable for large-scale projects.
- Non-Invasive: Lidar does not require physical contact with the target, making it ideal for sensitive environments.
Challenges and Limitations
- Cost: Lidar systems can be expensive, especially for high-resolution applications.
- Weather Conditions: Lidar can be affected by adverse weather conditions, such as fog or rain.
- Data Processing: Processing large amounts of lidar data can be time-consuming and computationally intensive.
In conclusion, Lidar has revolutionized 3D mapping and has become an essential tool in many industries. Its ability to provide accurate and detailed information about the Earth’s surface makes it a valuable asset for a wide range of applications.