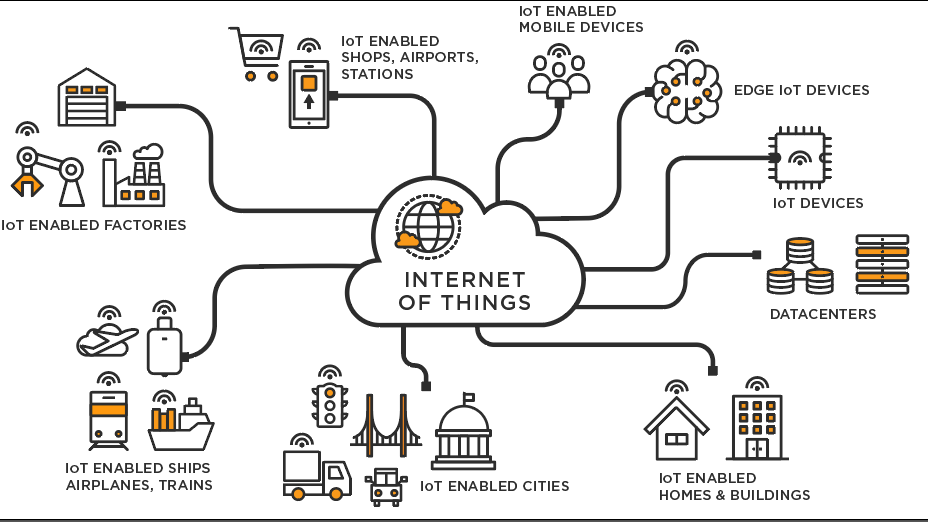
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the growing network of interconnected devices, vehicles, and appliances that are equipped with sensors, software, and network connectivity. These devices can collect and exchange data, enabling them to communicate and interact with each other.
Key Components of IoT:
- Devices: IoT devices can range from simple sensors to complex machines. Examples include smartphones, smart home devices, wearable technology, and industrial equipment.
- Connectivity: IoT devices are connected to the internet, allowing them to communicate with other devices and systems.
- Data: IoT devices collect and generate large amounts of data, which can be analyzed and used to improve efficiency, optimize processes, and gain valuable insights.
Applications of IoT:
- Smart Homes: IoT devices can be used to create smart homes that can automate tasks such as heating, lighting, and security.
- Healthcare: IoT devices can be used to monitor patients’ health, improve medical treatments, and reduce healthcare costs.
- Manufacturing: IoT can be used to optimize manufacturing processes, improve efficiency, and reduce waste.
- Transportation: IoT can be used to improve transportation systems, reduce traffic congestion, and enhance safety.
- Agriculture: IoT devices can be used to monitor crops, optimize irrigation, and improve agricultural productivity.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Security: Protecting IoT devices from cyberattacks is a major challenge.
- Privacy: The collection and use of data from IoT devices raises concerns about privacy and data security.
- Interoperability: Ensuring that different IoT devices can communicate and work together is another challenge.
- Economic Growth: IoT has the potential to create new industries and jobs, driving economic growth.
The Internet of Things is a rapidly growing field with immense potential. As IoT technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and transformative applications in the years to come.